Microsoft Search shows the content that your organization has stored in Microsoft 365 Tenant or indexed through connectors.
Microsoft Graph connectors can index third-party data to appear in Microsoft Search results. The third-party data can be hosted on-premises or in the public or private clouds. Connectors expand the types of content sources that are searchable in your Microsoft 365 productivity apps and the broader Microsoft ecosystem.
In this article, let's understand how to index "Azure DevOps" items using Graph Connector into Microsoft Search Results.
Note
The Azure DevOps connector supports only the Azure DevOps cloud service.
License requirements
To view data from connectors in your search results, users must have one of the following Microsoft 365 or Office 365 subscriptions,
- Microsoft 365 or Office 365 Enterprise E3 or E5
- Microsoft 365 or Office 365 Education A3 or A5
Lets start configuration steps,
Step 1 - Navigate to Connectors
- Go to Microsoft 365 admin center.
- In the navigation pane, go to Settings.
- Select > Microsoft Search.
- Select > Connectors
- Select > + Add
Step 2 - Select Azure DevOps as data source
Microsoft has seven connector avaible to connect with external datasource and several partner released connector to connect with external datasource.
Step 3 - Fill connection name details
- Name (mandatory)
- Connection Id (mandatory)
- Description (Optional)
Step 4 - Configure settings
AzureDevOps Organization -> Login to https://dev.azure.com and sign in with your orgnaization account. You can create new organization name or use existing one if exists.
Select Authentication Type as "Work or School Account"
You must register an app in AzureDevOps so that Microsoft search app can access the instance. Do use below information to complete the registration.
Navigate to https://app.vsaex.visualstudio.com/app/register
| S.NO | Fields | Values | Description |
| 1 | Company Name | Use Appropriate Name | This is the name of your company. |
| 2 | Application Name | Microsoft Search | This unique value identifies the application that you're authorizing. |
| 3 | Application Website | https://gcs.office.com/ | This required field is the URL of the application that will request access to your Azure DevOps instance during connector setup. |
| 4 | Authorization Callback Url | https://gcs.office.com/v1.0/admin/oauth/callback | A required callback URL that the authorization server redirects to. |
| 5 | Authorized Scope | Select the following scopes: Identity (read), Work Items (read), Variable Groups (read), Project and team (read), Graph (read) | This is the scope of access for the application |
As configuration details complete, you will navigate to below details; i.e. App ID & Client Secret.
Add generated App ID and Client Secret to complete authentication process.
Step 5 - Configure Data
Select project in the organization to crawl
Edit property, if you need to add more properties click preview > Next to proceed.
Step 6 - Manage Schema
You can choose which column can be set as Queryable, Searchable & Retrievable. It is standard schema configuration as SharePoint Search.
Step 7 - Manage Search Permission
You can choose to use the ACLs specified in the full crawl screen or you can override them to make your content visible to everyone
Step 8 - Content Refresh Settings
You can configure the incremental and full refresh interval.
Step 9 - Review connection and complete
All defined configurations can be reviewed and modified here. Once it completes, click to finish to proceed.
Step 10 - Review connection and complete
Wait for a couple of minutes and connection state will change from Publishing to Ready. Once connection state is ready, two actions need to be performed in sequence,
- Create Result Source.
- Create Vertical.
Result Type
A search result type is a rule that causes distinct kinds of search results to be displayed in different ways. It consists of the following,
- One or more conditions to compare each search result against, such as the content source of the search result.
- A result layout to use for search results that meet the conditions. The result layout controls the way that all results that meet the conditions appear and behave on a search results page.
Step 11 - Result Type Section
Once you select create result type, there will be simple steps to follow such as naming convention and entering the result type
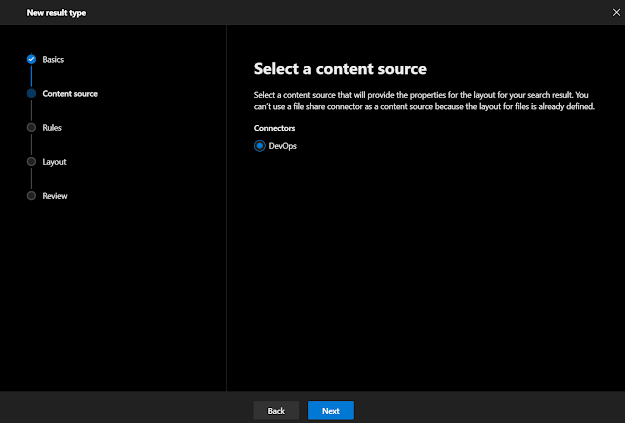
Step 12 - Result Type Content Source
Select appropriate content source, so that crawled or configured data can be mapped properly.
Step 13 - Design Layout
Once you click "Launch Layout Designer", it will navigate to https://searchlayoutdesigner.azurewebsites.net/
Step 14 - Search Layout Designer
Select blank layout and design the required card.
Copy content from Layout Payload editor and paste into step no. 13.
Layout payload editor added to github link
here
Step 15 - Review the resut type settings
Review the result type configuration and proceed to Vertical creation to map with defined result type.
Manage Vertical
Verticals make it easier for users to find the information that they have permission to see.
You can add search verticals that are relevant to your organization. These will appear on the Microsoft Search results page in SharePoint, Office, and Bing.
Before you start, make sure that the connector has been indexed. This can take up to 48 hours, depending on the file size.
You can’t create a vertical for content that resides in SharePoint.
There are three basic steps to add a vertical,
- Create the vertical. In this step, you define the vertical’s name, content source, and scope of the content to search.
- Define what the results for this vertical will look like.
- Enable the vertical (to be displayed) from the vertical list page.
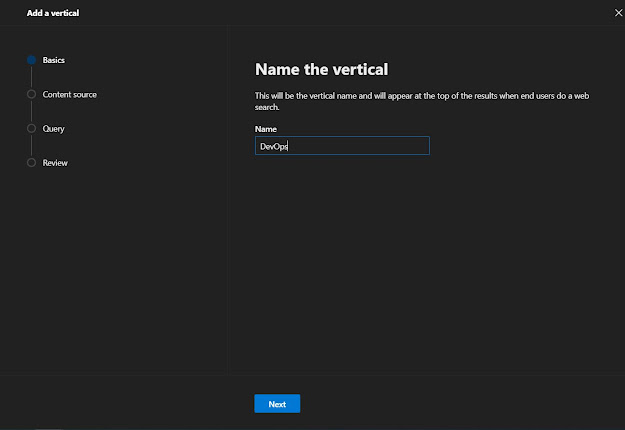
Step 16 - Create Vertical
In the navigation pane, go to custom connector, and then select the Verticals Link.
To add a vertical, select Add. Or, to edit a vertical, select it in the list.
Remember, verticals are created in a disabled state. They must be enabled before users can see them.
Step 17 - Connect Vertical with Content Source
Step 18 - Review and Add Vertical
Outcome
Azure Devops Data Screen Shot,
Microsoft Search Result from DevOps,
Related Article:-
I hope you have enjoyed and learned something new in this article. Thanks for reading and stay tuned for the next article.